Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
So much has been written about Quality Assurance that we should ask ourselves if we haven’t lost our understanding of this term. I can’t resist the assumption that each IT project is said to have an elite Quality Assurance unit, composed of software testers only, responsible for ensuring software quality in the project. In addition, HR units only add to this impression when they search for: “QA Specialists”, offering them jobs that focus on reporting tests and reporting defects.
By reading the piece below:
- You will learn the differences between Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC)
- You will learn the proposed scope of activities in IT projects that will shed more light on QA and QC
Differences between the Quality Assurance and Quality Control processes
What’s the source of these differences? First and foremost, Quality Assurance covers all activities carried out under a project. This starts with cooperation with the client (transparent communication), defining the roles and responsibilities in the team (defining the modus operandi, communication, defining the software development process), and ends with the definition of requirements and their life cycle.
The process includes all project participants, giving them the opportunity to influence the shape and definition of quality. This is based on the project’s context and its business value. We should remember about the possibility of measuring and assessing the quality of software at the same time.
The QA process is a preventive measure oriented largely toward the entire production process, both in the company and in the project at hand.
Now, Quality Control focuses largely on the search for errors/ irregularities in the functioning of the application by testing the software at various test levels and using various test types. These are activities that verify and validate the product in terms of compliance with the user’s requirements and expectations. Much of the responsibility lies with the software tester. This is a detective activity.
The illustration below shows the proportion between the activities around software testing and the entire quality assurance process.

A different look at the Quality Assurance process
This chart can be used as a “StarterPack” for understanding the Quality Assurance process and the role of the tester. It won’t fit every situation, but it can help you see quality assurance through the prism of increased activity in the project.
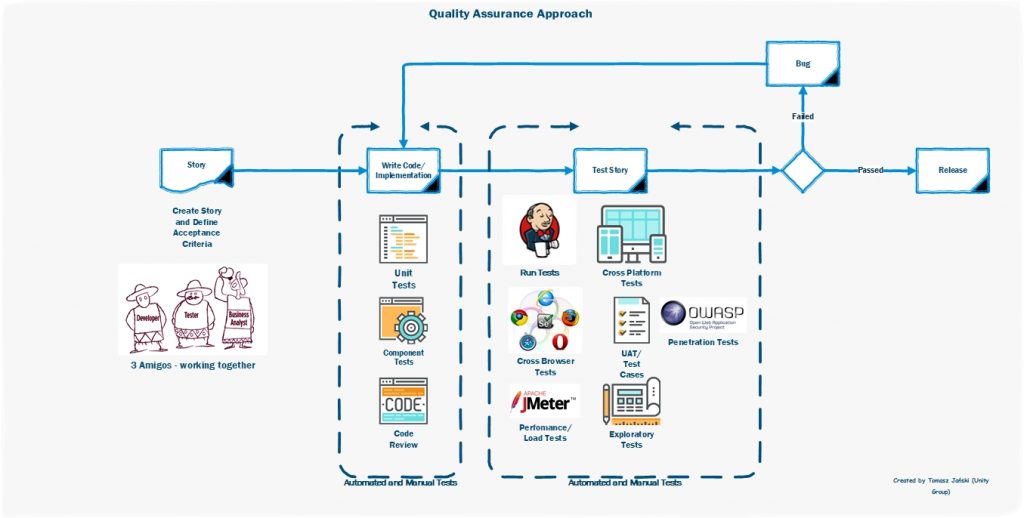
Let’s start from working with requirements. (Find out more about the term “3 Amigos” here).
In the context of software quality, we must bear in mind the beginning of a close cooperation between the 3 Amigos. We have three roles here as presented below:
1. Business analyst –this role may vary from one case to another, but this must surely be a person from the business, e.g. Product Owner.
2. Programmer.
3. Software tester.
In the model described, the three people fulfilling the above functions work together to define the Requirements (Story). This is an important moment when each party presents its point of view and how it understands individual functionalities (a confrontation of visions about the Requirements). A quick feedback loop and mutual understanding appear at this stage. “We don’t talk after implementing the functionality, we talk before that”. Such actions have a major preventive effect on the project and often reveal many risks that haven’t materialized yet, so the cost of their mitigation might be lower.
Example questions, e.g. from the perspective of a software tester:
– What does the client need this functionality for?
– What are the mock-ups, if there are any? 🙂
– Does the new requirement affect other components in the application?
Understandably, each party will have a different set of questions. Consequently, there should be a common understanding as to the product/ value to be delivered.
Once we know the expected deliverables and outputs, we move smoothly to the stage of implementation of the requirements. At this stage, we can use many methods to improve the software quality, ranging from good practices in relation to design, through to application writing and a set of test-oriented activities:
– unit test coverage of a % of the code,
An interesting part of this stage of work is the inclusion of the pyramid of automated tests, which might slightly influence the shape and scope of our tests.
The next steps in the process are the activities that are usually assigned to broadly understood software testers. This is a set of activities related to software verification/ validation, in terms of the above requirements, as well as areas related to quality characteristics (e.g. performance and security).
What’s next?
Quality Assurance is more than just software testing. Keep that in the back of your head and share this responsibility with the whole team. By inviting and engaging your team members in defining activities around software, make sure that your clients can subscribe to Gucci’s motto: “Quality is remembered long after the price is forgotten”.
If you want to learn more about quality management in IT, you should take a look at our publications on agile and software development practices.







